Heart Health Unveiled: Understanding the Risks of Cardiovascular Conditions
Written by: Cayla Jarvis
Graphics by: Arthur Perpall III & Lauryn Perpall
Introduction
The human heart is a remarkable organ that sustains life by pumping blood throughout our bodies, while also facing threats from cardiovascular conditions.
It is beneficial to learn about the complexities of cardiovascular health, uncover its functions, explore various conditions, and discuss prevention and management strategies.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of cardiovascular health.
Have you experienced sensations where your heart races uncontrollably, or so slowly that you begin to feel faint? These symptoms could indicate Arrhythmia.
Understanding cardiovascular diseases can help you take better care of your heart.
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is the result of an irregular heartbeat, which occurs when the electrical impulses in your heart misfire. Bradycardia refers to a heart beating too slowly, while tachycardia describes a heart beating too quickly or irregularly.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis may include a combination of physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), and other cardiac testing.
Treatments may include medications, lifestyle changes, and implant devices (pacemakers or defibrillators).
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the heart muscle, causing the muscles to thicken where blood is unable to pump to the rest of the body.
Symptoms:
● Fatigue
● Chest pain
● Shortness of breath
Causes of Cardiomyopathy:
● Genetics
● Diabetes
● Autoimmune disorders
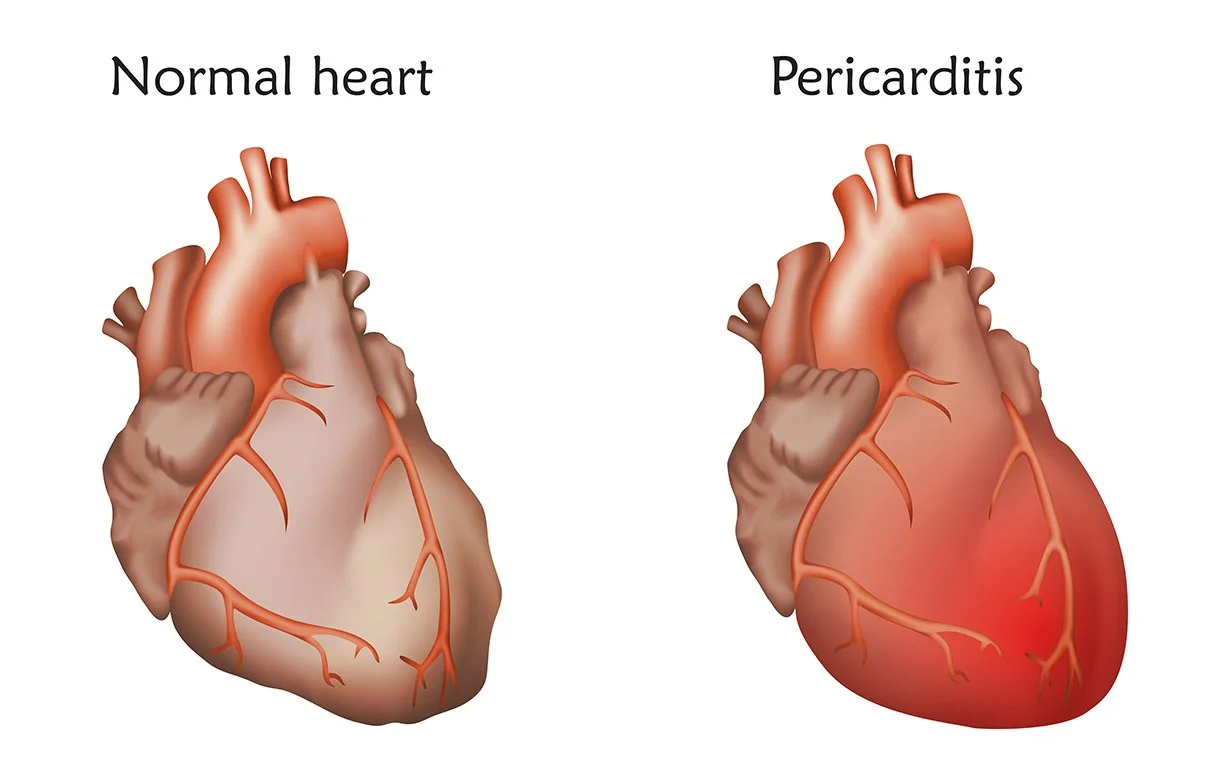
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a disease that causes inflammation of the pericardium (a layer of tissue filled with fluid that surrounds the heart to hold it in place and function).
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis can involve
Electrocardiogram (ECG): a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in the heart.
Chest X-ray: can show changes in the size and shape of the heart.
Echocardiogram: uses sound waves to show how blood flows through the heart and heart valves.
Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan: a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body.
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a type of diagnostic test that can create detailed images of nearly every structure and organ inside the body.
Treatments may include medication and rest.
Symptoms include:
● Chest pains
● Fevers
Causes of Pericarditis:
● Autoimmune disorders
● Heart attack
● Kidney failure
● Trauma
Coronary Artery Disease
A common heart condition when primary blood vessels are not properly receiving blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the heart. This disease begins when cholesterols and fats enter the walls of the heart.
Symptoms:
● Chest pain
● Shortness of breath
● Fatigue
● Heart Attack
Risk Factors:
● Age
● Sex - Men are at greater risk. However, after menopause women’s chances of developing coronary artery disease increase
● Family history
● Obesity
● Alcohol use
● High blood pressure
● High cholesterol
Prevention:
● Maintain a healthy diet
● Exercise
● Control high cholesterol and high blood pressure
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted or reduced, leading to damage to brain cells.
Common Symptoms
● Numbness on one side of the body
● Difficulty understanding speech
● Trouble with vision
● Headaches with no cause
● Dizziness or loss of balance
Diagnosis and Treatment
Treatments may include medication to dissolve blood clots, procedures to remove blockages, or blood pressure management.
Unraveling Family Health: A Revelation in September 2023
Interviewer: What influenced your interest in heart conditions?
Cayla: In September 2023, my grandfather's sudden hospitalization shocked us all.
He experienced chest pains and soaring blood pressure, revealing a series of mini-strokes that had quietly impacted his health, affecting his vision and coordination.
Interviewer: How did your family respond to this situation?
Cayla: We were deeply shaken. As we navigated his condition, we uncovered a hidden link in our family history: my grandfather's mother had battled strokes in her early 50s, suggesting a potential genetic connection.
Interviewer: What did this discovery mean for you and your family?
Cayla: It underscored the importance of understanding our familial health legacy.
We realized our health is intertwined with our lineage, guiding us toward informed and proactive choices.
Overall, the main ways to prevent heart disease include:
1. Healthy Eating: Adopting a balanced diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium while rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity most days of the week, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
3. Avoiding Tobacco: Refraining from smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke.
4. Limiting Alcohol: Drinking alcohol in moderation, if at all, which generally means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
5. Managing Stress: Employing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or hobbies to alleviate stress levels.
6. Monitoring Health: Regularly checking blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight, and seeking medical advice for any concerning symptoms or conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the risks and symptoms of cardiovascular diseases is crucial for maintaining heart health. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical attention, you can take proactive steps to protect your heart and live longer healthier lives.